Extracorporeal
Shockwave therapy (ESWT)
Can address pain and tissue repair associated with:
-
Musculoskeletal conditions including chronic tendinopathies and Myalgia
- Osteoarthritis
- Spasticity
- Wounds and ulcers *
- Urology *
(*Focus Shockwave)


How does it work?
A shockwave has two physical effects: the direct generation of mechanical forces (primary effect), and the indirect generation of mechanical forces by cavitation (secondary effect).
The primary effect is created by a sharp rise in positive pressure and the secondary effect during the resulting negative phase (tensile phase).
Secondary effect : INDIRECT MECHANICAL FORCE, the CAVITATION - the rapid formation, expansion, and subsequent implosion of air bubbles due to the negative pressure. The process in which the growth and collapse of acoustic waves including shock waves induce bubbles in liquid is called acoustic cavitation. Acoustic cavitation not only breaks calcific deposits, but also excites nerves, stimulates axons, and reduces pain. The energy released from the bubble during its collapse (implosion) create micro jets of water with high temperatures. This action has a damaging effect, which at low energy will cause micro tissue damage that will also instigate the healing process.
Cells react to these pressure changes in a process known as Mechanotransduction. Mechanotransduction, by definition, is the “mechanism by which cells convert mechanical stimuli into cellular responses to a variety of mechanical loads”. As a result, we find increased cell proliferation, differentiation, angiogenesis, collagen synthesis, increased expression of TGF-1 and MMP (Matrix metalloproteinases) molecules all assisting to expedite the healing process.

Want to learn more?
Watch our webinar on Current concepts for treating back pain with Shockwave Therapy on the Enovis Institute
Watch WebinarChattanooga ESWT benefits
Shockwave therapy uses pressure sound waves to treat various musculoskeletal pathologies. Therapeutic shockwave devices impart energy levels that are 1,000x more powerful than standard therapeutic ultrasound waves.
ENERGY FLUX DENSITY (EFD: IN MJ/MM2)
- Therapeutic effect is dependent on the energy distribution over a given area
- Most often quoted measure in research studies
- Different EFD values influence different tissular effects.
- The shape design and material of a variety of transmitters will determine the amount of EFD produced.
CHATTANOOGA RADIAL SHOCKWAVE DEVICES
Constant and controlled level of energy throughout the life of the handpiece. Our technology ensures high contact energy level during treatment (thousands of shocks):
Transmitters
- Optimal transmission vs absorption
- Large range of transmitters to deliver wide choice of EFD, wave profiles and applications
Projectile and tube engineering
- Reproducible speed
- Perfect fit in the tube
Values technology (compressed air system)
Therapeutic penetration depth 6cm (7.6cm in research)
Comfort mode (RPW2 only) unique automatic energy ramp up to provide better patient comfort
V-actor Handpiece
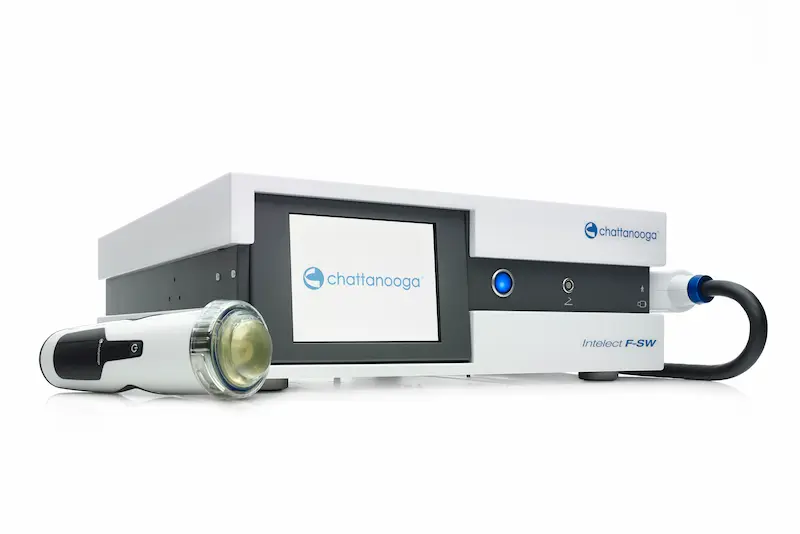
CHATTANOOGA FOCUS SHOCKWAVE DEVICES
- Enhanced Energy: 0.01 - 0.55mj/mm² Greater stimulation of metabolic change
- Broad Range Range: 1 - 8Hz Customize treatment to patient needs
- Intuitive and Easy to use: Protocols library and LCD touchscreen
- Patient comfort and efficacy
- 12.5cm penetration with pinpoint focus Greater depth to treat more indications